Landscaping Mississauga Gardens – Sumac
Large shrubs for dry soil – sumac
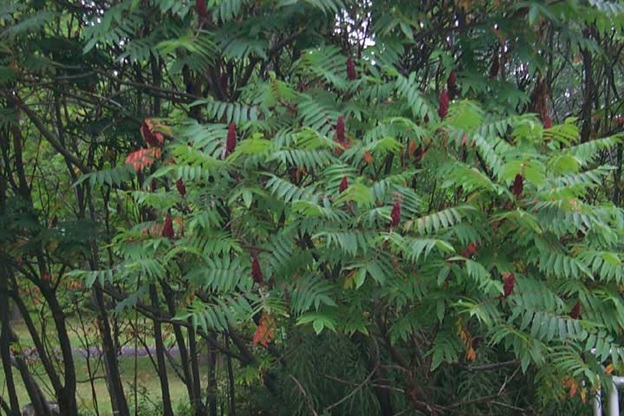
Depending upon whom you ask, sumac (sometimes spelled, “sumach”) is considered either a small tree or a tall shrub. Regardless in what category the plant is put, it certainly outperforms the largest trees with its fall colourful foliage. Dense stands of sumac trees covering a slope next to some Ontario highways in a sea of red, are some of the best fall foliage spectacles we witness each year. Despite their beauty sumacs recently became less popular. This is due to the confusion resulting from the fact that apart from the delightful and harmless sumacs, there also exists in the wild a poisonous version of the species that can cause a severe skin irritation when touched. Poison sumac, however, is in a distinct minority amongst the sumacs. The remaining sumac trees and shrubs produce no poison, but provide spectacular autumn color.
Additionally, it is easy to distinguish poison sumacs from their non-poison sumac relatives in the fall, when the berries have ripened to maturity. The poisonous plants have white berries in the fall, and the berries hang down. Non-poison sumacs bear red berries and their berries grow upright. In addition, poison sumac plants grow almost exclusively in swamps, whereas non-poison sumac plants prefer precisely the opposite habitat — soils that are well-drained and many are drought- tolerant. To avoid any confusion it is best to buy sumacs from nurseries.
One of the most popular sumacs in the GTA area is staghorn sumac, a tough plant that can be grown in dry areas of the garden. It is a relatively tall, tree-like variety that can reach up to 25 feet in height. Staghorn derives its name from the hairy texture of its branches, reminiscent of the velvety feel of deer antlers. The smooth sumac tree (Rhus glabra) is another common variety; it attains a height of about 10 feet. Both provide striking fall foliage.
As mentioned at the outset, the fall foliage they provide is unsurpassed. Nor is their autumn color display limited to their leaves, for the tuft atop the plant that holds sumac’s berries is red and fluffy, increasing the plant’s visual appeal. An added bonus is the fact that this seed-tuft remains on the sumac trees all winter, attracting colorful wild birds, whose presence greatly enhances the color and variety of winter scenery. Increasingly, homeowners begin to understand the importance of achieving four seasons of visual interest on the landscape and sumac is perfect for that as adequate winter scenery is perhaps the most difficult to achieve, since vegetation is more robust in the other three seasons.
Sumac seeds are an important source of bird food, precisely because they do stay on the plant long enough to be part of your winter scenery. This makes them an excellent emergency food for birds throughout the winter and beyond. I have witnessed bluebirds, black-capped chickadees and robins feeding on sumac seeds throughout the whole winter and into early spring today.